|
|
- HOME
-
General
- About
- Pediatric Anesthesia Fellowship Program
- Pediatric Anesthesia Resident Rotation - Goals and Objectives
- Fellowship Orientation (password required)
- Fellowship Goals and Objectives
- GME Policies (password required)
- Milestones
- Revised Case Logs
- Case Minimums
- Fellow Index Cases
- Pediatric Anesthesia Certification Examination
-
Clinical Information
- What makes Pediatric Anesthesia Different?
-
Pediatric OR Setup HOME
>
- STEP-2 PEDI OR SETUP - BREATHING CIRCUIT
- STEP-3 PEDI OR SETUP - SUCTION
- STEP-4- PEDI OR SETUP - OR TABLE AND PROPS
- STEP-5- PEDI OR SETUP - MONITORS
- STEP-6 PEDI OR SETUP - AIRWAY SETUP
- STEP-7 PEDI OR SETUP - MEDICATION DESKTOP
- STEP-8 PEDI OR SETUP - IV TRAY AND LINE
- STEP-9 PEDI OR SETUP - ACCESSORIES
- STEP-10 PEDI OR SETUP - SUMMARY
- The Pediatric Anesthesia Cart
- Pediatric Normal Parameters and Equipment
- Premedication
- Drug Library
- Standard Drug Dilutions in the Pediatric OR
- Pediatric Airway Management >
- Pediatric IV Insertion Technique
- Perioperative Fluid Therapy >
- Blood Transfusion Therapy >
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Single Lung Ventilation (SLV) Techniques
- Regional Anesthesia >
-
PEDI STAT
- PALS ALGORITHMS
- Newborn Resuscitation Algorithm
- PALS Cardiac Arrest
- PALS Tachycardia with a pulse and poor perfusion
- PALS Bradycardia with a pulse and poor perfusion
- Cardioversion / Defibrillation
- Laryngospasm
- EZ-IO Intraosseous Infusion System
- Hyperkalemia
- Anaphylaxis
- Malignant Hyperthermia
- Society for Pediatric Anesthesia - Pedi Crisis® Critical Events Checklist
- Case Primers
- Multimedia Library
- Pediatric Anesthesia Handicraft
- Robert N Reynolds, MD Award
- Disclosure Notice
- COVID-19 RESOURCES
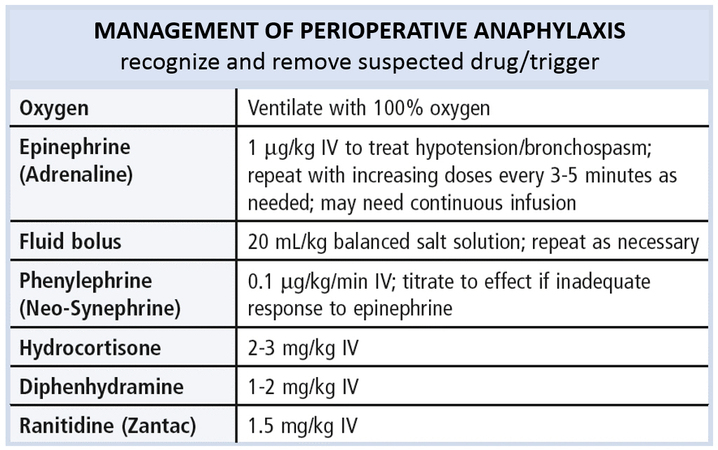
Anaphylaxis and Anesthesia
Perioperative anaphylaxis can be a life-threatening clinical syndrome involving multiple organ systems. The most commonly involved agents in perioperative anaphylaxis are NMBAs, latex,
and antibiotics. Anaphylaxis usually occurs shortly after induction, with NMBAs or antibiotics being primarily
involved, but anaphylaxis may occur any time with all potentially
allergenic agents. Dyes, hypnotic agents, local anesthetics, opioids,
colloids, aprotinin, protamine, chlorhexidine, and contrast agents are less
frequently involved. Latex-induced anaphylaxis usually occurs up to 30–60
min after the beginning of the surgery but may occur immediately.
External Links
Seattle Children's Hospital Anaphylaxis Clinical Pathway
Copyright © 2014. Aman Kalra, MD Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology, Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine (Author, Illustrator and Web Designer)
800 Washington Street, Box 298, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA 02111. USA
800 Washington Street, Box 298, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA 02111. USA
LAST UPDATED November 26th, 2023